Causes of Gum Disease and Effective Treatment Options
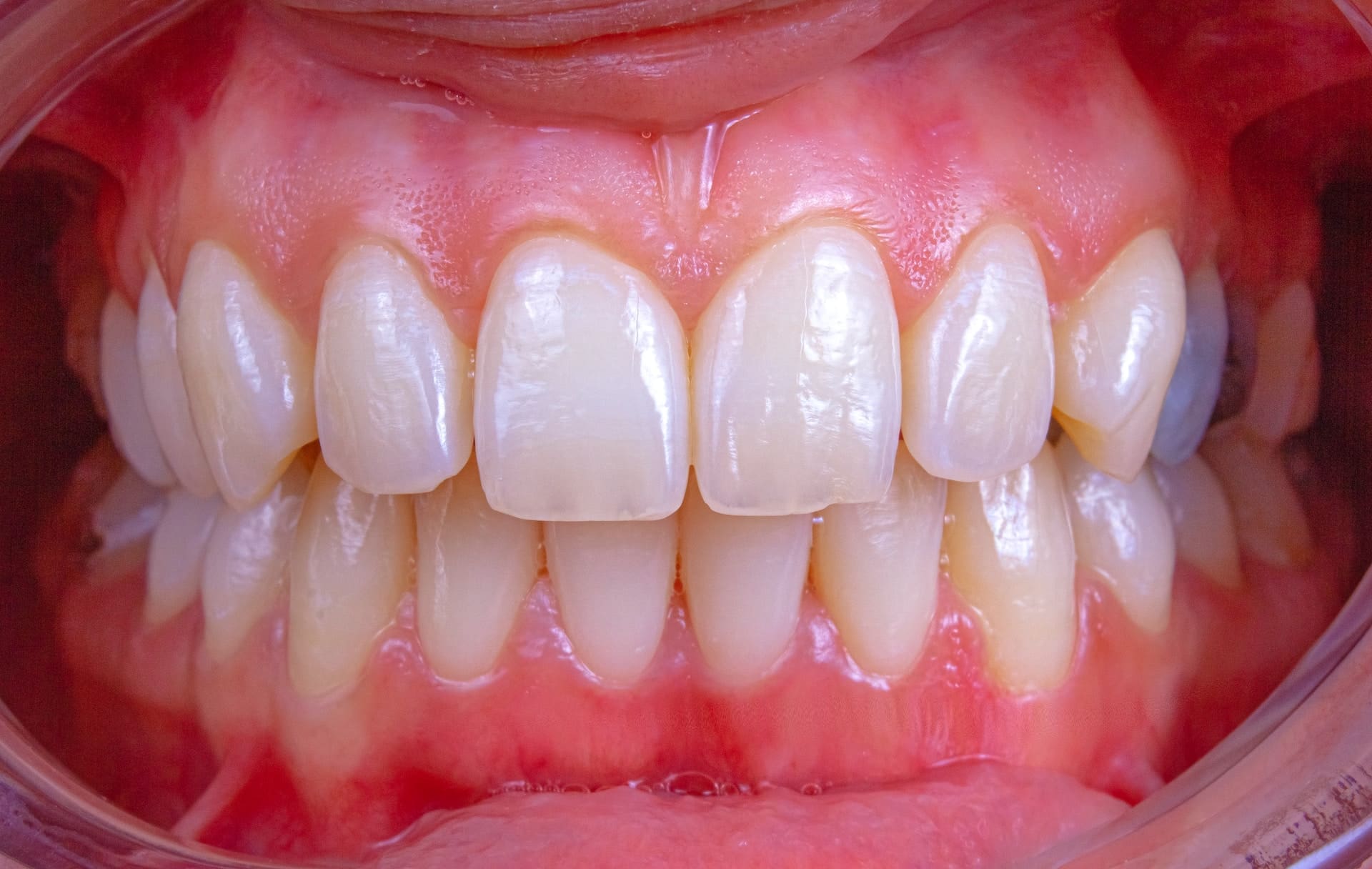
Gum disease is a widespread oral health issue that affects people all over the world. Oral health is crucial to people’s overall well-being. It is a chronic disorder that, if left untreated, can result in gum inflammation and tooth loss.
The causes of gum disease are varied, and effective treatment options depend on the severity of the disease and the individual’s overall health. Understanding the causes of gum disease and the available treatment options is crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing serious complications.
The causes of gum disease are examined in this article, along with the efficient management and prevention strategies for this widespread oral health issue.

